We first made the mechanistic connection between cardiac hypertrophy, apoptotic cardiomyocyte death, and progression to heart failure in 1998 (Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:10140-10145, 1998, pdf) (Figure 1), and subsequently identified Bcl2 family member Nix as the critical transcriptionally-induced mitochondrial pathway effector of apoptosis in cardiac hypertrophy (Nat Med. 8:725-730, 2002, pdf).
Figure 1.
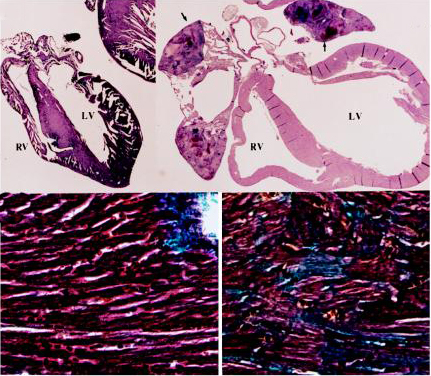
Characteristics of peripartum cardiomyopathy in Gαq-overexpressing mice. (Top) Gross morphology (4×) of peripartum nontransgenic (Left) and Gαq-overexpressing (Right) mouse hearts showing cardiomyopathic dilatation of cardiac chambers (LV, left ventricle; RV, right ventricle) with mural thrombi in atria (arrows). (Bottom) Trichrome stain (400×) of hearts depicted inb shows interstitial fibrosis and myocyte replacement (blue-stained cells), without inflammation in transgenic heart (Right).
Work in the laboratory that combined mechanistic studies of Nix and engineered Nix mutants in tissue culture with molecular and physiological studies of conditional and conventional gene knockout or conditional cardiac-specific transgenic mice has since described the exact role of Nix and related Bnip3 in cardiac remodeling after pressure overload hypertrophy and myocardial infarction injury. Ongoing work follows upon our recent observation that Nix is targeted in part to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mediates ER-mitochondrial cross talk that leads to programmed necrosis (J Clin Invest. 119:203-212, 2009, pdf).
Figure 2.
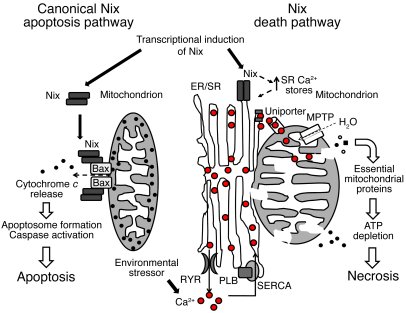
Mechanisms of Nix-mediated cell death